Easy scalable and fault tolerant structured streaming from kafka to spark
In this blog post, I will explain about spark structured streaming. Let’s first talk about what is structured streaming and how it works?
Structured Streaming is a scalable and fault-tolerant stream processing engine built on the Spark SQL engine. In short,_ Structured Streaming provides fast, scalable, fault-tolerant, end-to-end exactly-once stream processing without the user having to reason about streaming._The Spark SQL engine will take care of running it incrementally and continuously and updating the final result as streaming data continues to arrive.
Let’s say you want to maintain a running program data received from Kafka to console(just an example). Below is the way of express Structured Streaming.
First, create a local SparkSession, the starting point of all functionalities related to Spark.
val spark = SparkSession.builder
.master("local[*]")
.appName("app-name")
.config("spark.executor.cores", "2")
.config("spark.executor.memory", "4g")
.getOrCreate()
Next, let’s create a streaming DataFrame that represents data received from a Kafka server.
/**
Specify one or more locations to read data from
Built in support for Files/Kafka/Socket,pluggable
Can include multiple sources of different types using union()
*/
val upstream = spark.readStream
.format("kafka")
.option("kafka.bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092")
.option("subscribe", "test-topic")
.option("startingOffsets", "earliest")
.load()
This upstream DataFrame represents an unbounded table
containing the streaming data.This table contains seven column data named key,
value, topic, partition, offset, timestamp and timestampType.
Each streaming data becomes a row in the table.
The upstream DataFrame has the following columns:
| key(binary) | value(binary) | topic(string) | partition(long) | offset(long) | timestamp(long) | timestampType(int) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [binary] | [binary] | “topicA” | 345 | 1486087873 | ||
| [binary] | [binary] | “topicB” | 3 | 2890 | 1486086721 |
For more information, you can visit on Spark-Kafka structured streaming options.
val data = upstream.selectExpr("CAST(value AS STRING)")
val downstream = data
.writeStream
.format("console")
.start()
downstream.awaitTermination()
So now you have transformed DataFrame one column named “value” by Casting binary value to string and injected console sink. All data coming from Kafka will print on the console.
Here is an example that will receive data from multiple Kafka topics and will partition data by topic name.
val spark = SparkSession.builder
.master("local[*]")
.appName("app-name")
.config("spark.executor.cores", "2")
.config("spark.executor.memory", "4g")
.getOrCreate()
val checkpointLocation = "/tmp/temporary-" + UUID.randomUUID.toString
val upstream = spark.readStream
.format("kafka")
.option("kafka.bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092")
.option("subscribe", "test,Airport,Airports,Carriers,Planedata")
.option("startingOffsets", "earliest")
.load()
.selectExpr("topic", "CAST(value AS STRING)")// Transform "topic" and "value" columned
val downstream = upstream
.writeStream
// Partition by topic. it will create directory by topic name opic=Airport,topic=Carriers,topic=Planedata
.partitionBy("topic")
.format("csv")
.option("path", "/tmp/data")
.outputMode("append")
.trigger(ProcessingTime(3000))
.option("checkpointLocation", checkpointLocation)
.start()
downstream.awaitTermination()
Here is complete source code.
Basic Concepts:
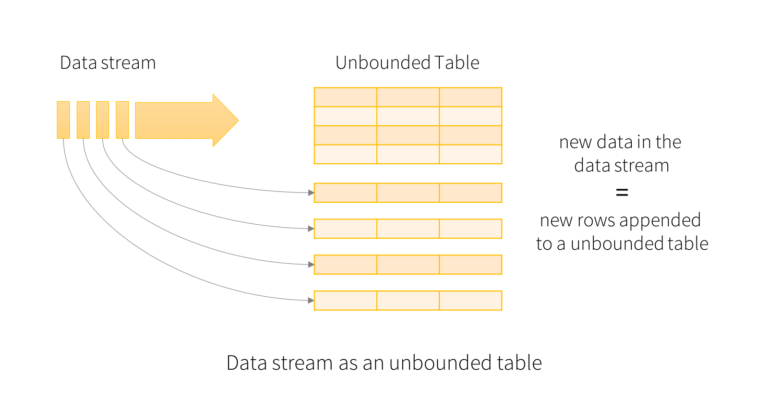
A query on the input will generate the “Result Table”. Every trigger interval (say, every 1 second), new rows get appended to the Input Table, which eventually updates the Result Table. Whenever the result table gets updated, we would want to write the changed result rows to an external sink.
Note that Structured Streaming does not materialize the entire table.
Input Sources: There are a few built-in sources.
File source – Reads files written in a directory as a stream of data. Supported file formats are text, csv, json, parquet.
Kafka source – Reads data from Kafka. It’s compatible with Kafka broker versions 0.10.0 or higher.
Socket source (for testing) – Reads UTF8 text data from a socket connection. The listening server socket is at the driver. Note that this should be used only for testing as this does not provide end-to-end fault-tolerance guarantees.
Rate source (for testing) – Generates data at the specified number of rows per second, each output row contains a timestamp and value.
There is a lot to explain about structured streaming, so I can not write everything in the single post but hope you get a basic idea of how structured stream works with Kafka.
References:
Structured Streaming Programming Guide
Structured Streaming + Kafka Integration Guide (Kafka broker version 0.10.0 or higher)